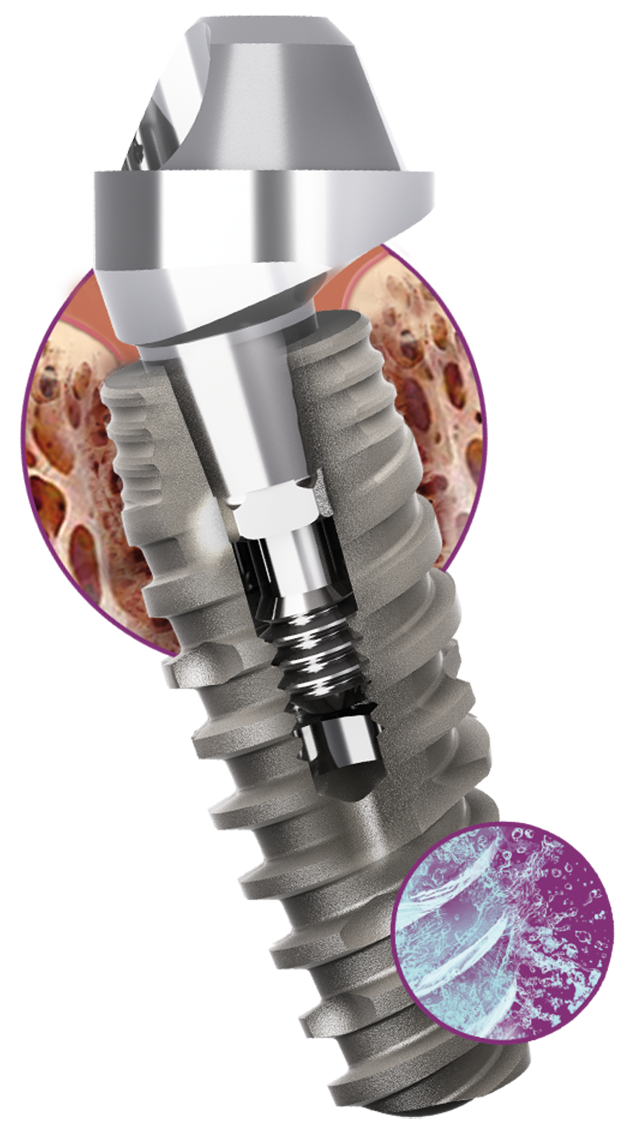
NeoArch™ offre des solutions immédiates, fiables et de qualité optimale pour les cas édentés fixes en se basant sur des concepts de produits éprouvés à un coût abordable.
La forte stabilité permet un fonctionnement immédiat
- Corps conique et filetage progressivement carré pour fournir une excellente stabilité mécanique initiale.
Double filetage pour une insertion plus rapide de l'implant.
- Acqua, la surface hydrophile conçue pour augmenter la mouillabilité.

Acqua
Surface hydrophile
La connexion Cône Morse fournit une stabilité mécanique 2-3 et une étanchéité bactérienne dans des études in vitro 4
- La connexion Cône Morse profonde transfère la distribution de la charge de la base vers l'apex
et offre une forte résistance et une excellente stabilité de la partie secondaire.2-3, 11
Étanchéité conique conçue pour éviter la migration des bactéries dans l'implant..5
La connexion prothétique unique pour tous les implants quel que soit le diamètre ou le type de filetage, facilitant ainsi la gestion du portefeuille.
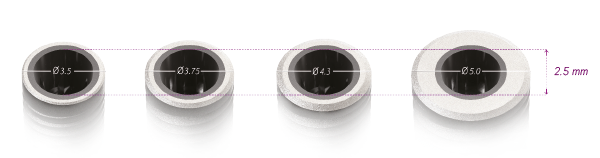
- Le concept de switching plate-forme a été démontré comme préservant le niveau osseux, soutenant ainsi le tissu péri-implantaire. 6-10
Partie secondaire conique Mini CM polyvalente
- Une large gamme d'options de hauteurs gingivales pour satisfaire les besoins de vos patients.
6 options pour la partie secondaire droite ; 3 options pour chacune des parties secondaires angulées 17° et 30°.
Les options de partie secondaire conique avec ou sans indice offrent la flexibilité
pour localiser la position finale.
La connexion Cône Morse améliore l'efficacité de la pose des parties secondaires des implants
et la stabilité.