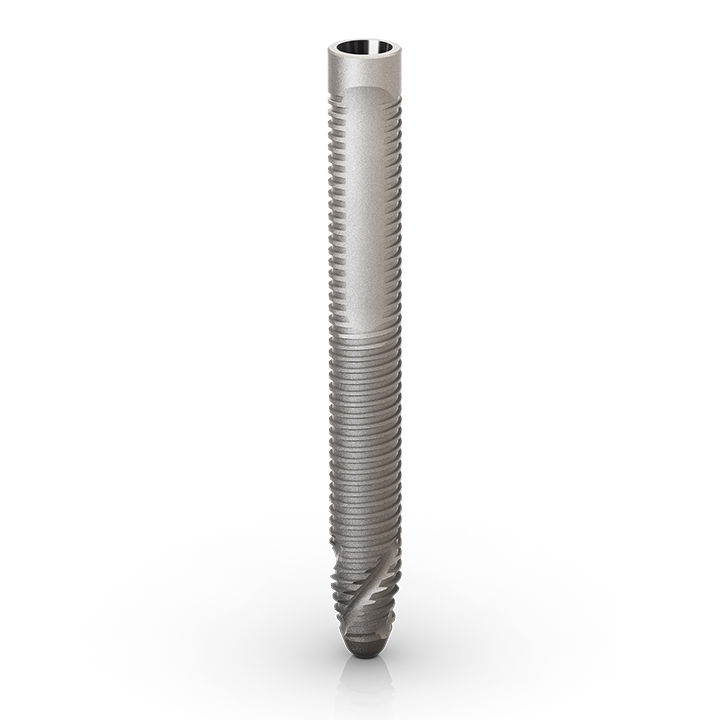
Zygoma GMTM
Implant for zygomatic anchorage
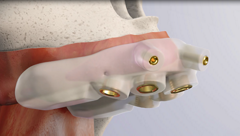
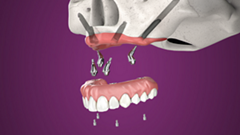
The zygomatic implants are specifically designed to bring surgical predictability to atrophic maxilla cases, as an alternative to grafting procedures.
The Neodent® Zygoma GMTM complement the standard implant system for achieving immediate loading protocol in fixed full-arch restoration. The solution combines the Grand Morse™ mechanical strength and the versatile prosthetic solutions. One prosthetic connection for all Grand Morse™ Implants: ease of use.
Features and Benefits
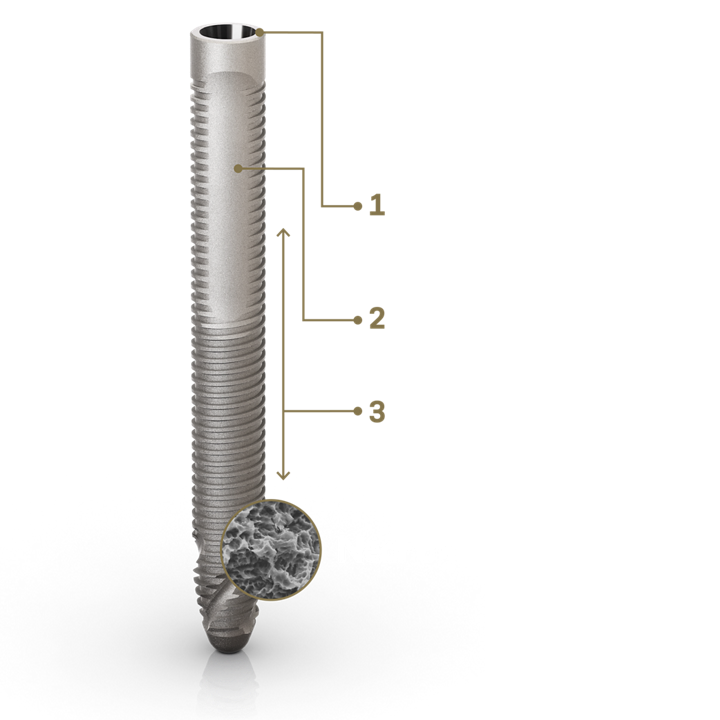

1. GRAND MORSE® CONNECTION
• All benefits of the original 16° Morse taper GM connection designed to ensure a tight fit for an optimal connection seal.
• Straight head designed to bring flexibility to the implant positioning.
2. IMPLANT DESIGN
• Tissue protect portion without threads for a friendly contact with the mucosa.
• Progressive increase of the thread depth at the apical area.
3. COMPREHENSIVE PORTFOLIO
• 4.0 mm of diameter.
• Ten different lengths: 30 / 35 / 37.5 / 40 / 42.5 / 45 / 47.5 / 50 / 52.5 / 55 mm.
Portfolio
See all GM Implants - A comprehensive implant portfolio designed for immediate protocols for all bone types