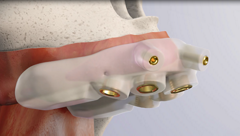
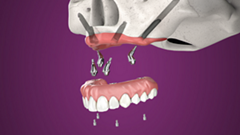
Immediate placement in challenging post extraction sockets
Immediate implant placement has gained attention since its offers the advantages of reducing surgical intervention and treatment compared to conventional placement.(1)
Post extraction areas with immediate implant placement in a multi-rooted molar involves anatomical challenges that may compromise primary stability or cause damage of neighboring structures.(2,3)
The Neodent® Grand Morse® Helix® implant Ø6.0 mm was developed to efficiently treat post extraction sockets and satisfy patient’s high expectations.
To reach the market needs, was expanded the Posterior Solution with more options for post-extraction sockets in molar regions. This is the reason why Neodent® Grand Morse® Helix® Ø7.0mm implant was developed as well.
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT WITH OPTIMIZED WIDE IMPLANT DESIGN
DELIVER NATURAL-LOOKING ESTHETICS THANKS TO AN OPTIMIZED WIDE EMERGENCE PROFILE DESIGN
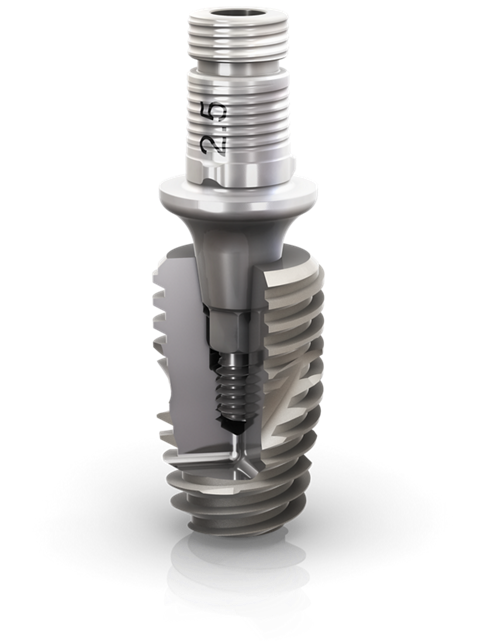


Designed to achieve high primary stability in wide post extraction sockets

Grand Morse™ Helix™ – The Unbeatable Versatility

A wide customizable healing abutment was designed to maintain the molar emergence profile

Consistent emergence profile for excellent esthetic outcomes
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT IN POST EXTRACTION SOCKETS WORKFLOW
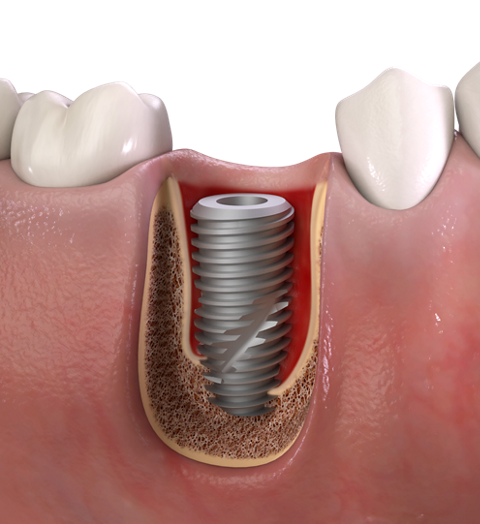
1. Molar extraction site
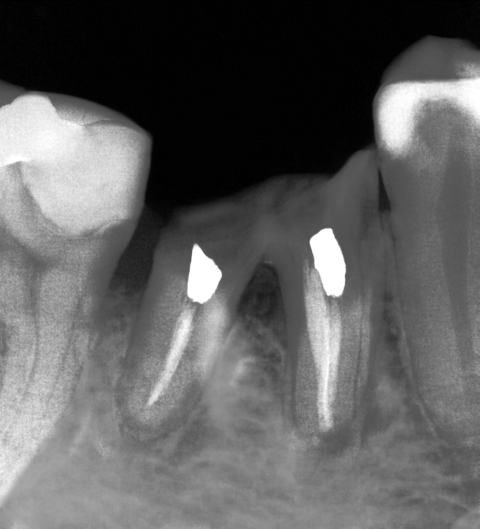
2. Multi-rooted extraction socket
3. Immediate implant placement with
Helix GM™ 6.0 or 7.0mm
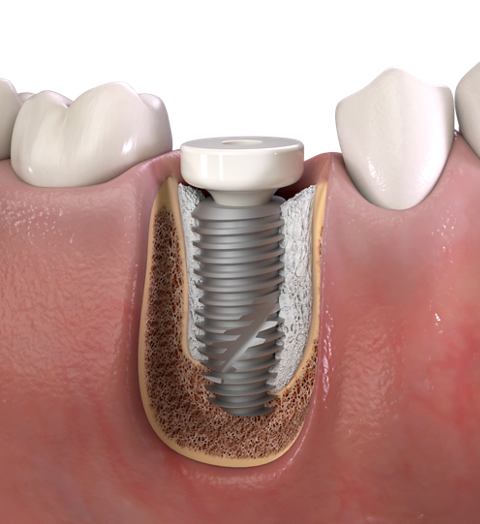
4. Customized natural-looking emergence profile using the wide customizable healing abutment
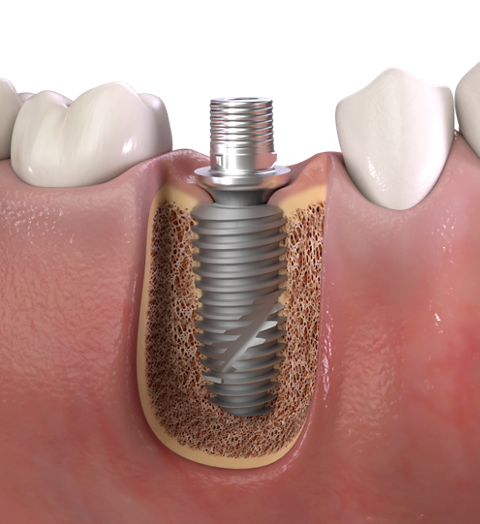
5. Wide Titanium Base abutment with consistent emergence profile
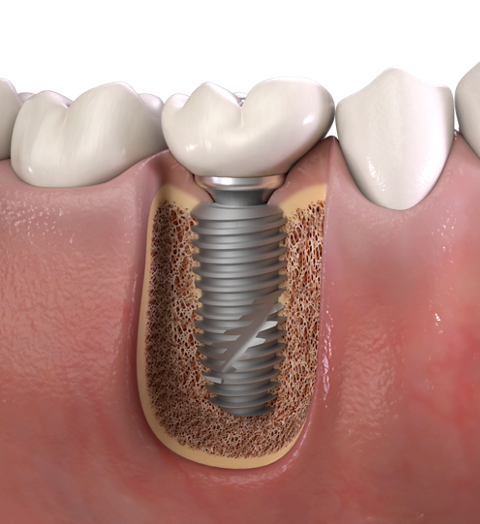
6. Digital or conventional
NEODENT® POSTERIOR SOLUTION OVERVIEW
SURGICAL
- Same Grand Morse™ Connection
- Same Grand Morse™ Surgical Kit and Instrumentals
- Same Grand Morse™ Prosthetic Kit and Drivers
Implants

8 mm

10 mm

11.5 mm

13 mm
Ø6.0mm / Ø7.0mm
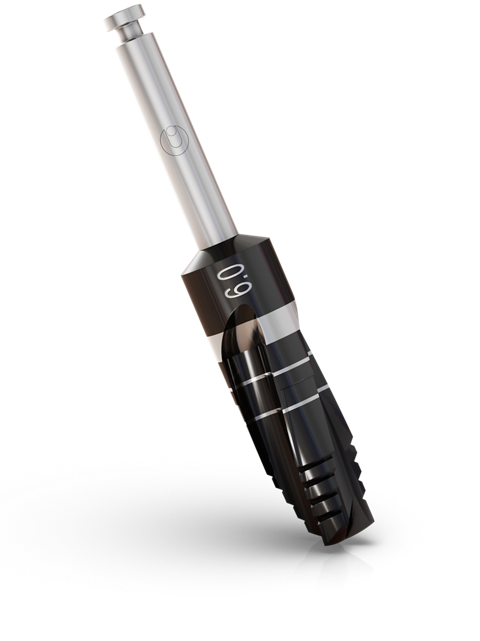

Ø6.0
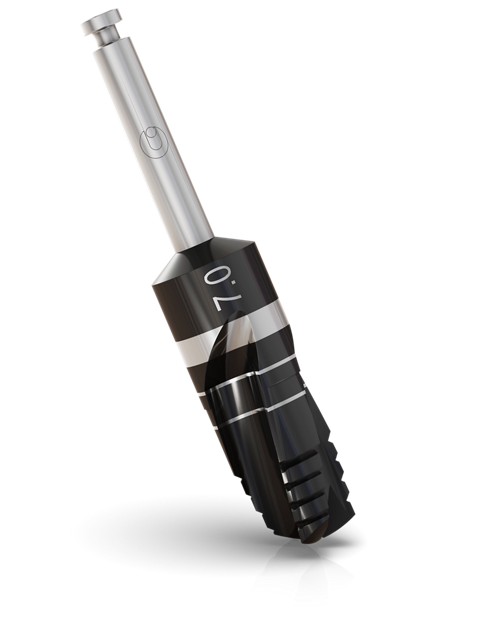

Ø7.0
Customizable Healing Abutments

| GH | 1.5mm | 2.5mm | 3.5mm | 4.5mm | 5.5mm | 6.5mm |
| Ø5.5 and Ø7.0 |
||||||

Neo Manual Screwdriver
PROSTHETIC
GM Titanium Base
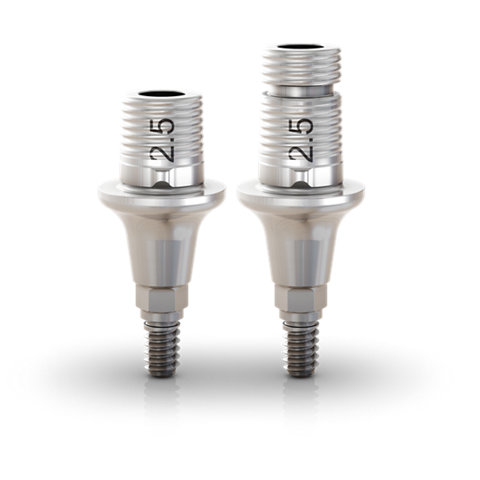

| GH | 0.8mm | 1.5mm | 2.5mm | 3.5mm | 4.5mm | |
| 4mm | Ø5.5 | |||||
| 6mm | ||||||
Use the Screwdriver Torque Connection - Torque Wrench
Final Restorations
Conventional

GM Titanium Base
Burn-out Coping
Ø5.5
4mm / 6mm
Digital

GM Hybrid
Repositionable Analog
Ø5.0/6.0