Zygoma GMTM
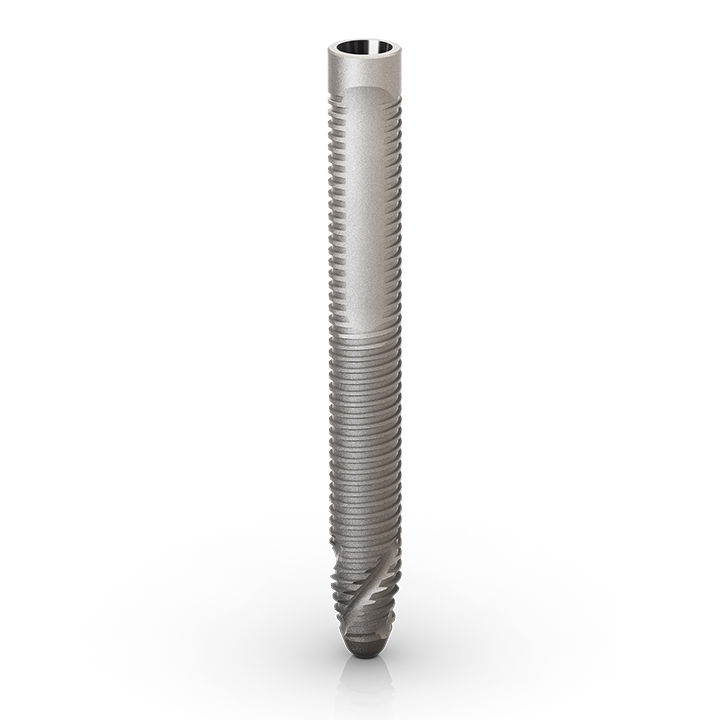
Implante para ancoragem zigomática
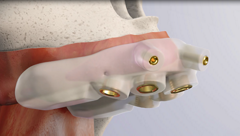
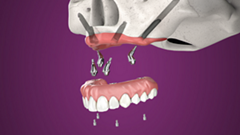
Os implantes zigomáticos são especificamente projetados para conferir previsibilidade cirúrgica aos casos de maxila atrófica, como alternativa aos procedimentos com enxertos.
O sistema Neodent® Zygoma GMTM complementa o sistema de implante padrão para se obter o protocolo de carga imediata na restauração fixa de arcada completa. A solução combina a resistência mecânica do Grand Morse™ e as soluções protéticas versáteis. Uma conexão protética para todos os Implantes Grand Morse™: facilidade de uso.
Características e benefícios
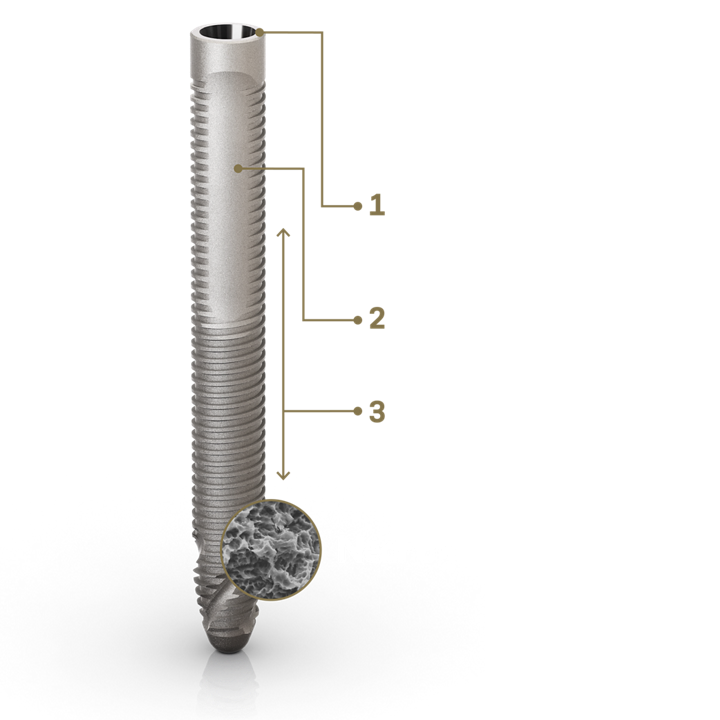

1. GRAND MORSE® CONNECTION
• Todos os benefícios da conexão GM de Cone Morse 16° original, desenvolvida para garantir o ajuste firme, para uma melhor vedação da conexão.
• Cabeça reta, desenvolvida para trazer flexibilidade ao posicionamento do implante.
2. DESIGN DO IMPLANTE
• Parte de proteção do tecido sem roscas, para um contato confortável com a mucosa.
• Aumento progressivo da profundidade da rosca na área apical.
3. PORTFÓLIO ABRANGENTE
• 4,0 mm de diâmetro.
• Dez diâmetros diferentes: 30 / 35 / 37,5 / 40 / 42,5 / 45 / 47,5 / 50 / 52,5 / 55 mm.
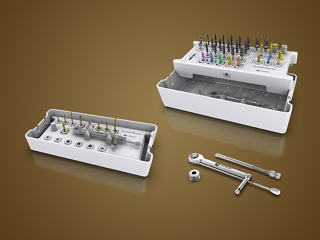
Portfólio
Veja todos os implantes GM - Um portfólio de implantes abrangente, desenvolvido para protocolos imediatos em todos os tipos de ossos