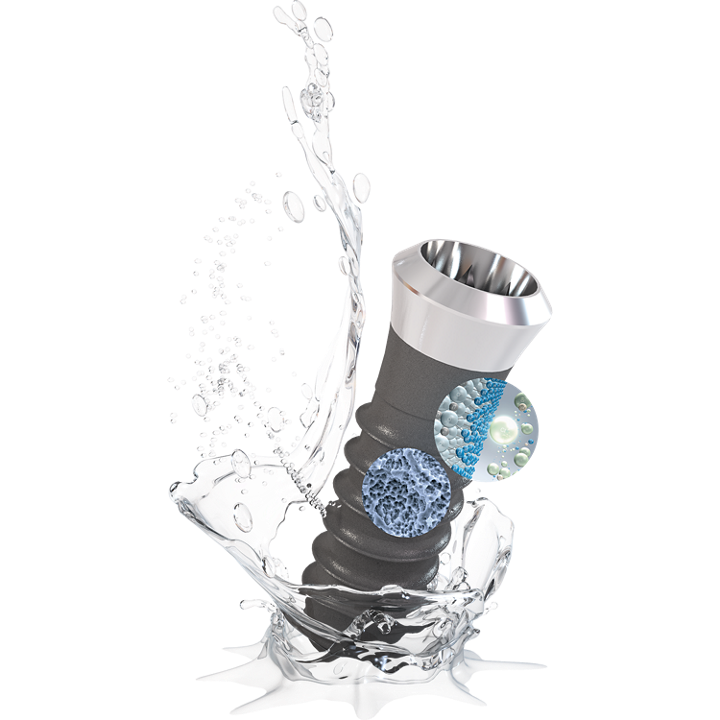
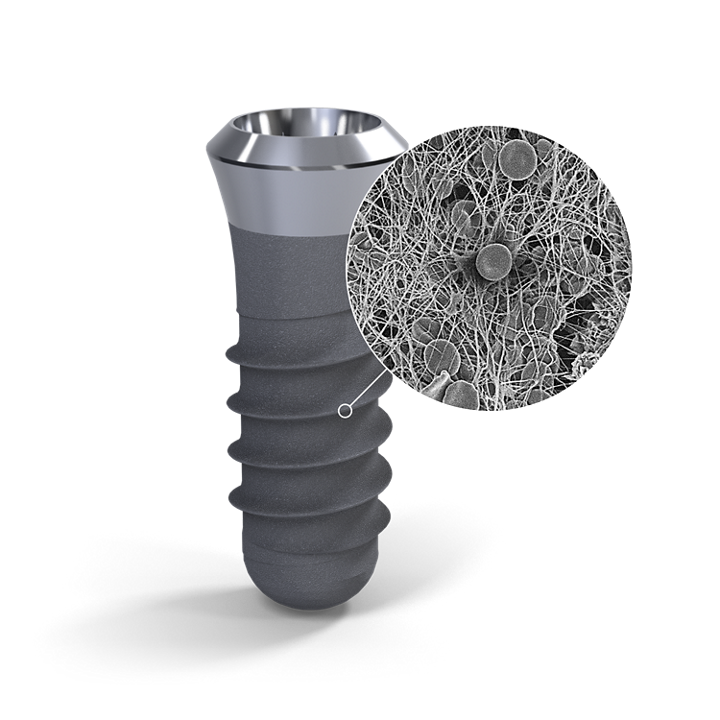
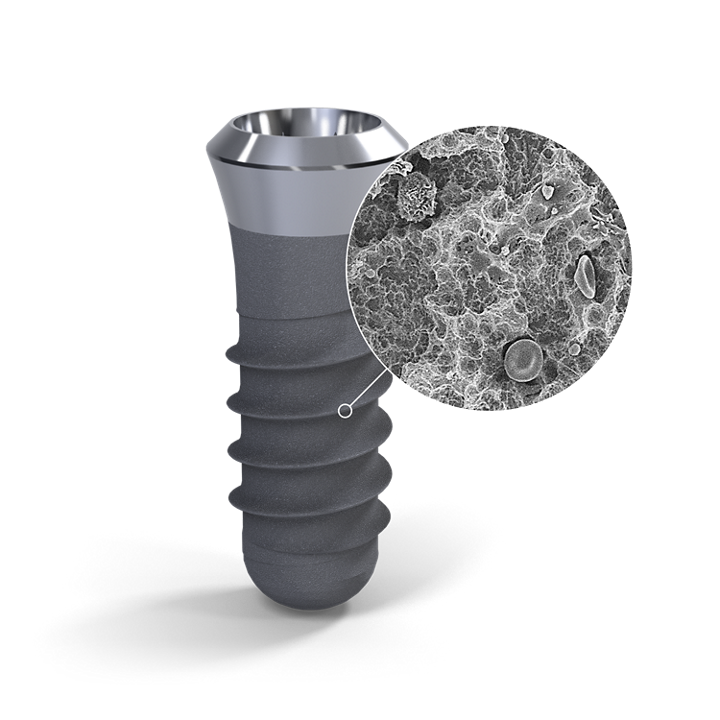
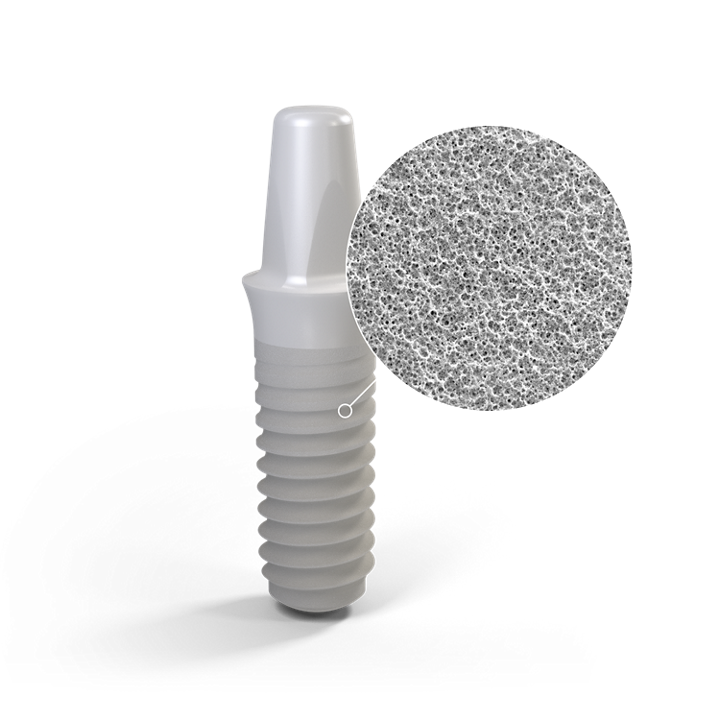
SLActive® 1 Straumann SLActive implants compared to Straumann SLA implants. Lang NP, Salvi GE, Huynh-Ba G, Ivanovski S, Donos N, Bosshardt DD. Early osseointegration to hydrophilic and hydrophobic implant surfaces in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011 Apr;22(4):349-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02172.x. 2 Rupp F, Scheideler L, Olshanska N, de Wild M, Wieland M, Geis-Gerstorfer J. Enhancing surface free energy and hydrophilicity through chemical modification of microstructured titanium implant surfaces. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research A, 76(2):323-334, 2006. 3 De Wild M. Superhydrophilic SLActive® implants. Straumann document 151.52, 2005; Katharina Maniura. Laboratory for Materials – Biology Interactions Empa, St. Gallen, Switzerland, Protein and blood adsorption on Ti and TiZr implants as a model for osseointegration. EAO 22nd Annual Scientific Meeting, October 17 – 19 2013, Dublin. Kopf BS, Schipanski A, Rottmar M, Berner S, Maniura-Weber K, Enhanced differentiation of human osteoblasts on Ti surfaces pre-treated with human whole blood. Acta Biomaterialia. 2015 June; 19: 180–190. Kopf BS, Ruch S, Berner S, Spencer ND, Maniura-Weber K, The role of nanostructures and hydrophilicity in osseointegration: In-vitro protein-adsorption and blood-interaction studies. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015 August; 103 (8): 2661-2672. 4 Schwarz, F., et al., Bone regeneration in dehiscence-type defects at non-submerged and submerged chemically modified (SLActive®) and conventional SLA® titanium implants: an immunohistochemical study in dogs. J Clin. Periodontol. 35.1 (2008): 64–75. 5 Rausch-fan X, Qu Z, Wieland M, Matejka M, Schedle A. Differentiation and cytokine synthesis of human alveolar osteoblasts compared to osteoblast-like cells (MG63) in response to titanium surfaces. Dental Materials 2008 Jan;24(1):102-10. Epub 2007 Apr 27. 6 Schwarz F, Herten M, Sager M, Wieland M, Dard M, Becker J. Histological and immunohistochemical analysis of initial and early osseous integration at chemically modified and conventional SLA® titanium implants: Preliminary results of a pilot study in dogs. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 11(4): 481-488, 2007. 7 Raghavendra S, Wood MC, Taylor TD. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2005 May–Jun;20(3):425–31. 9. 8 Oates TW, Valderrama P, Bischof M, Nedir R, Jones A, Simpson J, Toutenburg H, Cochran DL. Enhanced implant stability with a chemically modified SLA® surface: a randomized pilot study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2007;22(5):755–760. 9 Nicolau P, Guerra F, Reis R, Krafft T, Benz K , Jackowski J 10-year results from a randomized controlled multicenter study with immediately and early loaded SLActive implants in posterior jaws. Presented at 25th Annual Scientific Meeting of the European Association of Osseointegration – 29 Sep – 1 Oct 2016, Paris. 10 Nelson, K., Stricker, A., Raguse, J.-D. and Nahles, S. (2016), Rehabilitation of irradiated patients with chemically modified and conventional SLA implants: a clinical clarification. J Oral Rehabil, 43: 871–872. doi:10.1111/joor.12434. 11 Patients treated with dental implants after surgery and radio-chemotherapy of oral cancer. Heberer S, Kilic S, Hossamo J, Raguse J-D, Nelson K. Implantatgetragene Rehabilitation post radiationem unter Verwendung von Implantaten mit modifizierter und herkömmlicher sandgestrahlter, säuregeätzter Oberfläche: vorläufige Ergebnisse einer Split-Mouth-Studie. Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 22, 2011; 546–551. 12 Straumann (2016). SLActive® supports enhanced bone formation in a minipig surgical GBR model with coronal circumferential defects. Unpublished data. SLA® 13 Buser D, Janner SF, Wittneben JG, Bragger U, Ramseier CA, Salvi GE. 10-year survival and success rates of 511 titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: a retrospective study in 303 partially edentulous patients. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012 Dec;14(6):839-51. 14 Fischer K, Stenberg T.: Prospective 10-year cohort study based on a randomized controlled trial (RCT) on implant-supported full-arch maxillary prostheses. Part 1: sandblasted and acid-etched implants and mucosal tissue. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012 Dec;14(6):808-15. 15 van Velzen FJ, Ofec R, Schulten EA, Ten Bruggenkate CM,.10-year survival rate and the incidence of peri-implant disease of 374 titanium dental implants with a SLA surface: a prospective cohort study in 177 fully and partially edentulous patients. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015 Oct;26(10):1121-8. 16 Cochran DL, Jackson JM, Bernard JP, ten Bruggenkate CM, Buser D, Taylor TD, Weingart D, Schoolfield JD, Jones AA, Oates TW Jr. A 5-year prospective multicenter study of early loaded titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011 Nov-Dec;26(6):1324-32. 17 Cochran D, Oates T, Morton D, Jones A, Buser D, Peters F. Clinical field trial examining an implant with a sand-blasted, acid-etched surface. J Periodontol. 2007 Jun;78(6):974-82. 18 Bornstein MM, Schmid B, Belser UC, Lussi A, Buser D. Early loading of non-submerged titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface. 5-year results of a prospective study in partially edentulous patients. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005 Dec;16(6):631-8. 19 Roccuzzo M1, Aglietta M, Bunino M, Bonino L. Early loading of sandblasted and acid-etched implants: a randomized-controlled double-blind split-mouth study. Five-year results. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008 Feb;19(2):148-52. 20 Derks J, Schaller D, Håkansson J, Wennström JL, Tomasi C, Berglundh T. Effectiveness of Implant Therapy Analyzed in a Swedish Population: Prevalence of Peri-implantitis. J Dent Res. 2016 Jan;95(1):43-9. doi ZLA® 21 Bormann KH, Gellrich NC, Kniha H, Dard M, Wieland M, Gahlert M. Biomechanical evaluation of a microstructured zirconia implant by a removal torque comparison with a standard Ti-SLA implant. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012 Oct;23(10):1210-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02291.x. Epub 2011 Nov 14. 22 Gahlert M, Roehling S, Sprecher CM, Kniha H, Milz S, Bormann K. In vivo performance of zirconia and titanium implants: a histomorphometric study in mini pig maxillae. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012 Mar;23(3):281-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02157.x. Epub 2011 Aug 2. 23 Gahlert M1, Röhling S, Wieland M, Eichhorn S, Küchenhoff H, Kniha H A comparison study of the osseointegration of zirconia and titanium dental implants. A biomechanical evaluation in the maxilla of pigs. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2010 Dec;12(4):297-305. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2009.00168.x.
ZLA® 23 Roehling S, Astasov-Frauenhoffer M, Hauser-Gerspach, Braissant O, Woelfler H, et a., In Vitro Biofilm Formation On Titanium And Zirconia Implant Surfaces, J Periodontol. 2016 Oct 7:1-16. [E-Pub vor Print-Pub] DOI: 10.1902/jop.2016.160245